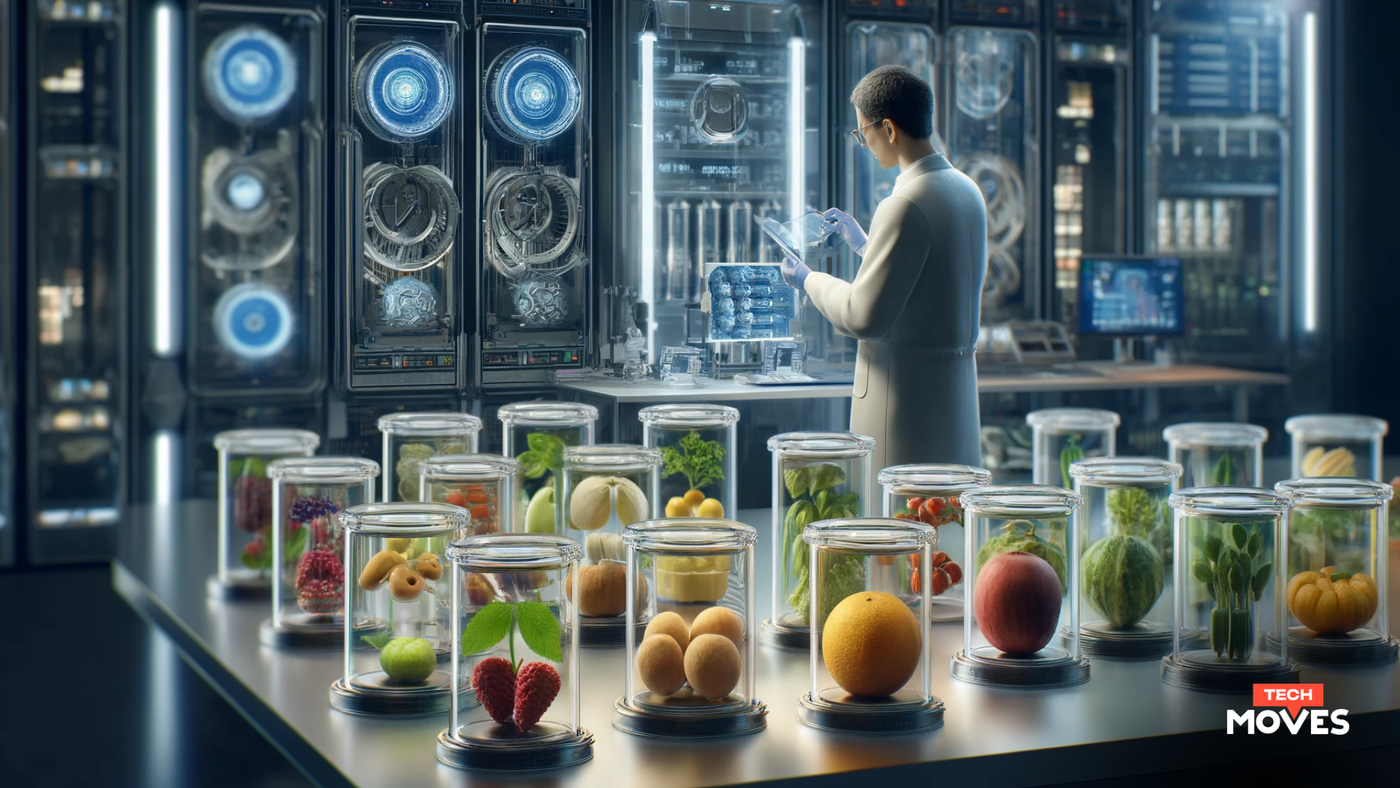
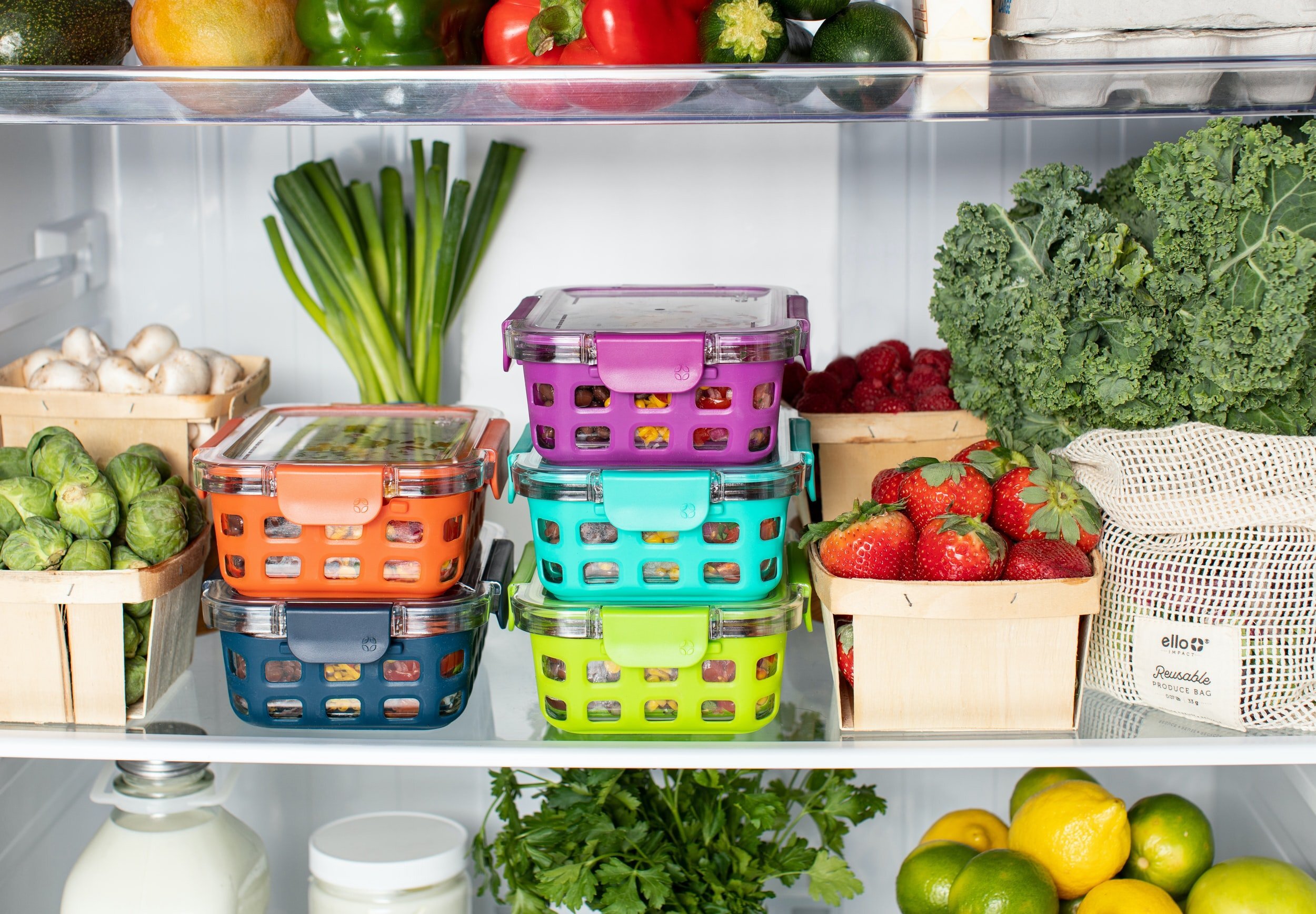
In a significant advancement for the agriculture and food industry, new technological solutions are emerging to enhance the shelf life of fruits and vegetables, addressing a critical issue of post-harvest losses. This innovation is set to revolutionize the way perishable produce is stored and transported, ensuring fresher produce reaches consumers and reducing food wastage.
The Problem of Post-Harvest Losses
Post-harvest losses of fruits and vegetables have long been a challenge in the agriculture sector. According to industry experts, a substantial portion of harvested produce is lost due to spoilage during storage and transportation. This not only results in financial losses for farmers and suppliers but also contributes to global food insecurity.
Emerging Technologies to the Rescue
Several innovative technologies are now being deployed to tackle this issue effectively:
-
Controlled Atmosphere Storage: This technology regulates the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen in storage environments. By maintaining optimal atmospheric conditions, the ripening process of fruits and vegetables is slowed down, thereby extending their shelf life significantly.
-
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): MAP involves altering the atmosphere inside packaging to prolong freshness. This method reduces the respiration rates of fruits and vegetables and delays spoilage. Advanced packaging materials that adjust gas levels dynamically are being introduced to further enhance the effectiveness of MAP.
-
Cold Chain Solutions: Advanced refrigeration systems and cold chain logistics ensure that produce is kept at optimal temperatures from farm to table. Innovations in cold chain technology, such as solar-powered refrigeration units and smart temperature monitoring systems, are making it more feasible to maintain consistent cooling, even in remote areas.
-
Edible Coatings: Scientists have developed edible coatings derived from natural substances such as chitosan, aloe vera, and essential oils. These coatings form a thin, protective layer around fruits and vegetables, reducing moisture loss and microbial growth. The coatings are safe for consumption and can be easily washed off.
-
Post-Harvest Treatments: Techniques such as hot water treatment, UV radiation, and the use of natural preservatives are being employed to kill pathogens and delay spoilage. These methods are gaining popularity due to their effectiveness and minimal impact on the nutritional quality of the produce.
Benefits of Technology Integration
Integrating these technologies offers several benefits:
- Reduced Food Wastage: By extending the shelf life of produce, these technologies minimize losses due to spoilage, ensuring more food reaches consumers.
- Economic Gains for Farmers: Farmers and suppliers can benefit from reduced losses and better prices for their produce, enhancing their overall profitability.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing food wastage also mitigates the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of spoiled produce, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Future Prospects
The adoption of these technologies is expected to grow as awareness increases and costs decrease. Governments and industry stakeholders are likely to invest more in research and development to further refine these solutions and make them more accessible to small-scale farmers and suppliers.
Conclusion
The implementation of advanced technologies to enhance the shelf life of fruits and vegetables represents a transformative step forward in the agriculture and food industry. By reducing post-harvest losses, these innovations not only boost economic returns for farmers but also contribute to global food security and environmental sustainability. As these technologies become more widespread, they hold the promise of a future where fresh, nutritious produce is available to more people around the world, all while reducing food wastage.