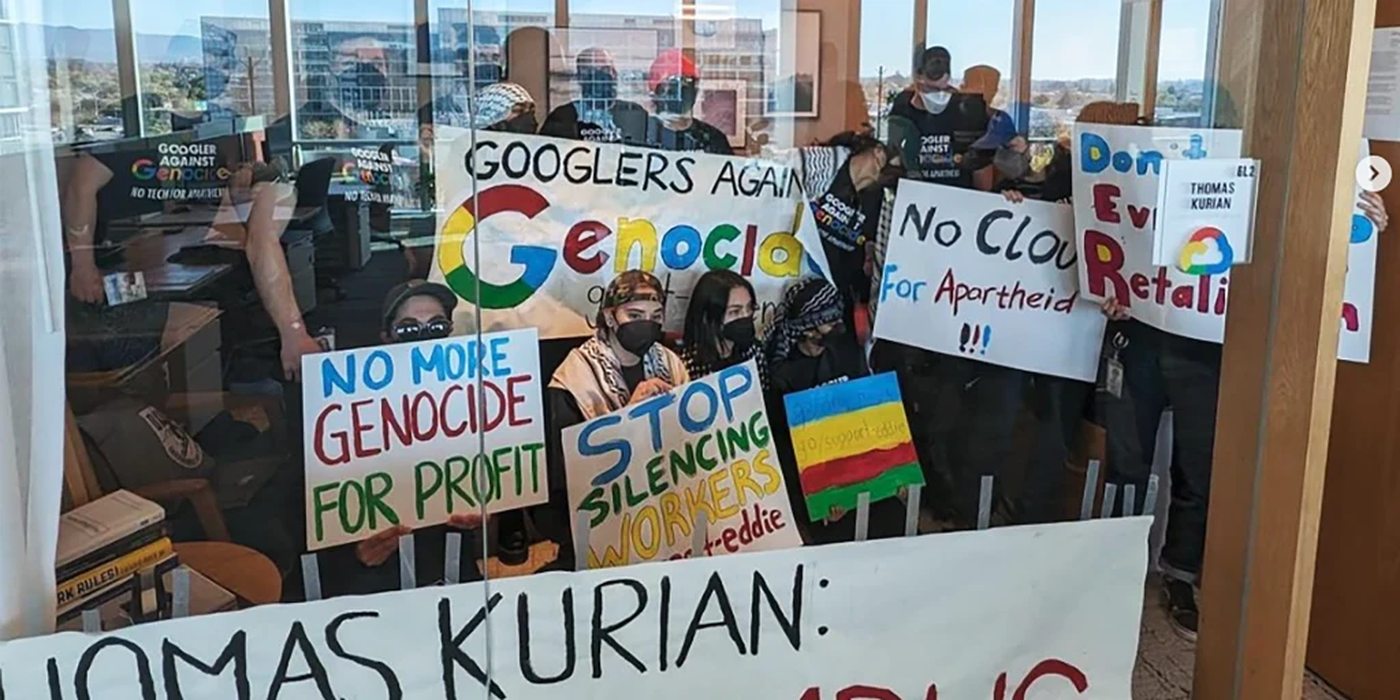
The recent firings at Google highlight a significant and controversial intersection between corporate operations and employee activism, especially regarding sensitive geopolitical issues. Google dismissed 28 employees who were reportedly involved in protests against the company's Project Nimbus contract with the Israeli government—a $1.2 billion agreement to provide cloud services.
Key Points of the Incident:
-
Employee Protests: The protests were in response to Google's involvement with Project Nimbus and the broader implications of technology companies' roles in political conflicts. Protests included sit-ins at Google's offices in New York and Sunnyvale, which led to the arrest of nine individuals.
-
Company's Response: Google cited violations of workplace policies, disruption of work, and concerns about the safety of other employees as reasons for the terminations. Chris Rackow, Google’s head of global security, emphasized in a memo that the behavior of the protesters was not only unacceptable but also disruptive and threatening to fellow employees.
-
Reactions and Backlash: The activist group No Tech for Apartheid accused Google of using the situation as an excuse to retaliate against peaceful protesters and to avoid addressing the ethical concerns related to Project Nimbus. The group labeled the firings as illegal and retaliatory, highlighting a disconnect between the company's actions and the protesters' accounts of the event.
-
Google's Workplace Policy: In response to the unrest, CEO Sundar Pichai reminded employees to refrain from bringing politics into the workplace, stressing the importance of maintaining a focus on the company's objectives and preserving a workplace culture conducive to productivity and innovation.
Broader Implications:
This incident at Google is part of a larger trend of tech employees voicing their concerns about how their work impacts broader societal and ethical issues. These events raise several critical points:
-
Corporate Responsibility and Ethics: Companies like Google are increasingly facing scrutiny over their contracts and the ethical implications of their technology applications, particularly in politically sensitive regions.
-
Employee Activism: There is a growing movement within tech companies where employees are not just advocating for internal changes (e.g., working conditions, diversity and inclusion) but are also challenging their employers' business decisions on ethical grounds.
-
Balancing Act for Companies: Organizations must navigate the complex balance between respecting employee rights to expression and activism, maintaining operational integrity, and adhering to corporate policies designed to ensure a safe and productive work environment.
-
Global Corporate Impact: Decisions made by multinational corporations like Google can have significant geopolitical impacts, influencing public perceptions and governmental relations.
Conclusion:
As technology companies continue to expand their influence globally, the decisions they make—whether in product development, contracts, or employee management—can lead to significant ethical, social, and political consequences. Google's recent actions and the ensuing backlash underscore the challenges companies face in managing these dynamics while trying to maintain a focused and harmonious workplace. This situation also reflects the growing need for companies to develop clear policies that address both employee activism and corporate responsibility in a rapidly changing global environment.